Our global mindshare around environmental issues has reached unprecedented levels, causing a shift in how we weigh the convenience and versatility of everyday materials—like plastics—that are also major pollutants. The ubiquitous nature of plastics in our daily lives, coupled with their detrimental impact on the planet, has prompted a change in thinking in how we approach their production, consumption, and disposal.
Plastics have greatly contributed to innovation in many industries and increased convenience to consumers worldwide, but the harms of plastic pollution coupled with an increased carbon footprint has underscored the urgent need to find more sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives. With a better understanding of environmentally-friendly plastics, industry leaders can take the next step to reducing plastic pollution on a large scale. In this article, we will uncover the meaning behind sustainable plastics and the different options in the space that can fit any businesses production needs.
What Are Sustainable Plastics?
Sustainable plastics, also referred to as green plastics, bioplastics, or eco-friendly plastics, are often created from renewable resources or synthesized from a combination of traditional and plastic additives (compounds such as starch blends, bio-based polymers, or oxodegradable additives that can be mixed with traditional plastics to enhance their environmental performance). These plastics are designed to break down naturally over time and reduce the persistence of plastic waste in the environment. Sustainable plastics offer many ecological benefits, but their full impact depends on factors such as production processes, end-of-life management, and overall sustainability practices. Some of their benefits include:
Reduced Carbon Footprint: Sustainable plastics are often made from renewable resources such as cornstarch, sugarcane, or algae. These materials absorb carbon dioxide during their growth, which can help offset the emissions produced during their production and use, leading to a lower overall carbon footprint compared to fossil fuel-based plastics.
Decreased Dependency on Fossil Fuels: The production of traditional plastics relies heavily on petroleum, a non-renewable resource. Sustainable plastics can be derived from agricultural waste, plant-based feedstocks, or other renewable sources, reducing the demand for fossil fuels and decreasing the environmental impact associated with their extraction and processing.
Biodegradability and Compostability: Some sustainable plastics are designed to be biodegradable or compostable. This means they can break down naturally into non-toxic components under specific conditions, reducing the accumulation of plastic waste in landfills and oceans.
Positive Consumer Perception: As environmental awareness grows, consumers are becoming more conscious of their purchasing choices. Companies that use sustainable plastics in their products may benefit from a positive image and enhanced brand loyalty.
Regulatory Support: Some regions are implementing regulations and policies aimed at reducing plastic pollution and promoting the use of sustainable materials. This can create a favorable environment for companies to adopt sustainable plastics into the manufacturing of their goods.
The general opinion of sustainable plastics is positive. This is reflected by the continued growth of this industry, with the global market for sustainable plastics reaching 319 billion in 2022 and an expected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.7% from 2023 to 2030. As this industry continues to grow, we can expect to see great innovations for plastics as a whole.
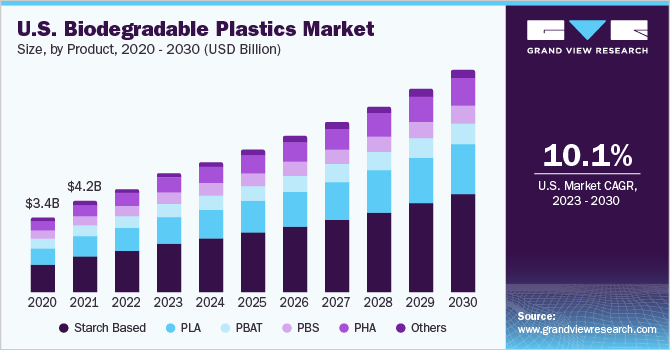
What’s the Difference Between Biodegradable and Recyclable Plastics?
Although both biodegradable and recyclable plastics are sustainable, it’s important to understand what each is and how they can contribute to a more eco-friendly footprint across industries.
Biodegradable Plastics
Biodegradable plastics can break down naturally into non-toxic components over time when exposed to specific environmental conditions. Unlike traditional plastics, which can persist in the environment for hundreds of years and cause pollution, biodegradable plastics are designed to mitigate some of these environmental concerns by reducing the long-lasting impact of plastic waste. There are two main categories of biodegradable plastics:
Bio-based Plastics: Bio-based plastics are made from renewable resources, such as cornstarch, sugarcane, potato starch, or other plant-based materials. Polylactic acid (PLA) is one of the most common bio-based plastics. These plastics can degrade more easily because the source materials are organic in nature.
Petroleum-based Plastics with Additives: Conventional petroleum-based plastics like polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) are blended with additives that help them break down more quickly under specific conditions such as sunlight exposure or temperature.
Recyclable Plastics
Recyclable plastics are types of plastic materials that can be collected, processed, and reprocessed into new products through recycling processes. Recycling involves breaking down plastic waste into its original components or transforming it into new plastic products, reducing the need for new plastic material and conserving resources.
Common examples of recyclable plastics include:
- PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate): Used for water bottles, beverage containers, and food packaging.
- HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene): Used for milk jugs, shampoo bottles, and containers for household products.
- PP (Polypropylene): Used for yogurt containers, bottle caps, and various types of packaging.
- PS (Polystyrene): Used for disposable utensils, Styrofoam, and certain types of packaging.
What are the Differences Between Sustainable and Traditional Plastics?
As we experience the consequences of plastic pollution, consumers demand more responsible material choices, especially when it comes to plastics. It’s important to understand the key differences between sustainable and traditional plastic options as they both play an important part in consumer products today and in the future.
Raw Material Source:
- Sustainable Plastics: Produced from renewable resources such as plant-based feedstocks like corn, sugarcane, and algae. This greatly reduces the reliance on fossil fuels.
- Traditional Plastics: Primarily derived from non-renewable fossil fuels like petroleum or natural gas.
Environmental Impact:
- Sustainable Plastics: Typically have a lower carbon footprint and reduced environmental impact due to the use of renewable resources and sustainable production processes.
- Traditional Plastics: Contribute to pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and resource depletion associated with fossil fuel extraction.
Biodegradability:
- Sustainable Plastics: Some are designed to biodegrade under specific conditions, reducing their long-term persistence in the environment.
- Traditional Plastics: Generally do not biodegrade quickly, leading to accumulation of plastic waste in landfills, oceans, and ecosystems for hundreds of years.
Toxicity:
- Sustainable Plastics: Tend to have lower levels of harmful additives and chemicals, promoting safer use and disposal.
- Traditional Plastics: Can contain additives like Bisphenol A (BPA) that pose environmental and health risks.
Cost:
- Sustainable Plastics: May have higher production costs due to using renewable resources and innovative processes.
- Traditional Plastics: Generally have lower production costs due to established production methods and economies of scale.
Regulations and Policies:
- Sustainable Plastics: Many regions have begun encouraging or even mandating the use of sustainable materials to address plastic waste and environmental concerns.
- Traditional Plastics: Facing widespread scrutiny and regulation due to their environmental impact.
What Strategies can be Used to Increase the Adoption of Sustainable Plastics?
As we look to a future that is less reliant on traditional plastics, what steps are required to get there? Increasing the adoption of sustainable plastics requires a multi-faceted approach that addresses various public and private stakeholders, from government officials to consumers. Here are some of the strategies that can help promote more widespread understanding and urgency around this important issue.
Creating Education and Awareness Campaigns and Engaging Consumers:
- Creating educational campaigns to raise awareness about the environmental impact of traditional plastics and the benefits of sustainable alternatives.
- Providing clear information about the different types of sustainable plastics, their properties, and how they contribute to a circular economy.
- Engaging consumers through transparent labeling, indicating the use of sustainable plastics in products.
- Highlighting the positive environmental impact of choosing products with sustainable packaging.
Aligning Government Policies:
- Governments can implement regulations that encourage or mandate the use of sustainable plastics in specific applications, thereby creating a level playing field for businesses adopting these materials.
- Governments and organizations can also offer incentives, grants, or subsidies to businesses that invest in sustainable plastics technology or adopt eco-friendly practices.
Collaborating with Organizations and Businesses:
- Collaborating with industry associations, environmental organizations, and research institutions to collectively advocate for the adoption of sustainable plastics.
- Partnering with suppliers, manufacturers, and retailers to ensure a seamless supply chain for sustainable materials.
- Design products with recyclability, reusability, and compostability in mind, contributing to a circular economy where materials are kept in use and waste is minimized.
- Encouraging suppliers and manufacturers to adopt sustainable practices and materials throughout the supply chain.
- Share case studies and success stories of businesses that have successfully adopted sustainable plastics, demonstrating the benefits and positive outcomes.
Developing Superior Plastic Alternative
- Investing in research and development to improve the properties and cost-effectiveness of sustainable plastics, making them more attractive to businesses.
- Developing sustainable plastics that match or exceed the performance of traditional plastics, ensuring that businesses don’t have to compromise on quality when switching materials.
- Enabling a circular economy: designing products with recyclability, reusability, and compostability in mind, contributing to a circular economy where materials are kept in use and waste is minimized.
Creating a Culture of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR):
- Aligning business goals with sustainability by incorporating the use of sustainable plastics into corporate social responsibility initiatives.
- Developing effective communication strategies that highlight the environmental benefits, economic advantages, and long-term sustainability of adopting these materials.
- Demonstrating a long-term commitment to sustainability by setting clear goals for reducing plastic waste and continuously improving the adoption of sustainable plastic.
Create Sustainable Products With Nautical
For businesses looking for a sustainable alternative to their current products materials, working with Nautical can help make them take the necessary steps towards a more eco-friendly future. We have partnered with Polaris Trading Solutions to leverage the technology of Solmera™– the world’s most affordable perishable plastic solution. Solmera is an additive that is mixed in with traditional plastic pellets during the manufacturing process, requiring no change to existing factory configurations. In addition, it is also FDA and EU compliant as well as certified non-toxic, making it truly the perfect solution for almost any plastic product. By offering this environmentally friendly alternative to traditional plastics, we are allowing our customers to make a change and mitigate the impact of plastic waste on earth.




