Shipping costs are often one of the highest costs associated with ecommerce fulfillment and supply chain services. Many factors are driving shipping costs higher, such as inefficient cargo ships, global shipping container shortages, and a limited supply of commodities despite increased consumer demand.
While many global shipping cost factors are outside of a business’ control, that doesn’t mean they just have to accept the cut to profit margins. Fortunately for most businesses, third-party logistics (3PL) partners can do a lot to help reduce shipping costs through the optimization of information, orders, and shipping procedures. Let’s take a look at the methods 3PLs use to provide partners with better shipping rates, and what this means to your business bottom line.
How Carriers Set Shipping Rates
It helps to first understand how shipping rates are set. Shipping is complicated, and there are many factors that determine shipping rates. But the biggest cost considerations include the type of cargo, how it will be transported (truck, ship, train, aircraft), its weight, and the distance it needs to be delivered.
Freight rates are constantly fluctuating but always represent a large impact on a business’ bottom line. Here are many of the major factors influencing freight rates.
Distance
Unsurprisingly, the farther the distance a package needs to be shipped, the more expensive the shipping rate will be. Less trafficked areas will cost even more to ship to since it is less profitable for the carrier and may require them to partner with another carrier.
In the U.S., Shipping Zones factor heavily into delivery costs and are calculated using zip codes. The zones vary based on the distance from the origin of a shipment to its destination. The higher the zone, the higher the shipping cost.
- Zone 1: 1-50 miles
- Zone 2: 51-150 miles
- Zone 3: 151-300 miles
- Zone 4: 301-600 miles
- Zone 5: 601-1000 miles
- Zone 6: 1001-1400 miles
- Zone 7: 1401-1800 miles
- Zone 8: 1801 miles or greater
- Zone 9: US territories & some military addresses
Weight & Density
Weight and density are key factors that impact freight costs. Whether shipping by land, air, or sea, the more space and power needed to convey your goods, the more it’ll cost. Density is often expressed as pounds per cubic feet, and a density class assigned by dividing the weight of cargo by its volume. There are 18 possible classifications for LTL freight, ranging from a low rating of 50 (easily handled dense freight) to the highest rating of 500 (low density, high value). The higher the class, the less dense (and more expensive) an order is to ship.
Handling & Stowability
You’ve seen line item costs for “shipping and handling,” and this is the handling part. Handling also factors into an item’s freight classification. Fragile, oddly-shaped items may be given a different classification based on the more complex handling requirements. These items may require more people, specialized tools, or care. The easier it is for a carrier to handle your goods, the less it will cost to ship them.
Similarly, a good may be too bulky, unstackable, or other characteristics that make it difficult to load, and this can affect the class it falls into.
Liability
Goods that are fragile or high value will fetch a higher shipping cost since the carrier will have to pay more if held liable for theft or damage. The same applies if the shipped item is potentially hazardous or perishable.
Accessorials
These are additional fees assessed by carriers that require them to go beyond regular dock-to-dock pick-up and delivery duties. Some examples of accessorials include inside delivery, residential pick-up and delivery, weekend delivery, product palletizing, and gate service.
Base Rates
Every shipment is billed based on weight. A base rate is the way that LTL carriers calculate the gross freight charges of a specific shipment. For every 100 pounds being shipped, there is an associated cost (known as CWT or “hundredweight”), which equates to their base rate. If a carrier needs more volume or increases costs for lanes by balancing trucks and freight, they will often alter their base rate.
Example: You are shipping out a 300-pound fridge; the cost per CWT is $150. This would add up to 3 CWT which would equal $450.
Minimum Charge
LTL freight carriers have minimum shipping rates to ensure they remain profitable for operations in routes that may contain less cargo or be less populated. The minimum varies by carrier, and is sometimes referred to as Absolute Minimum Charge (AMC) or Minimum Floor Charge.
Navigating these rates and processes is a challenge for most companies. This is one of many ways that 3PLs can add value to a business. 3PL providers can leverage their partnerships and order volume to negotiate better shipping rates on behalf of their clients. By working with multiple carriers and consolidating shipments, 3PLs can often negotiate better rates than individual businesses.
How 3PLs Get Lower Shipping Rates
All of these costs add up, and while the supply chain often goes unseen to consumers, businesses need to carefully optimize supply chain costs to maximize profitability. Since shipping is one of the biggest bottom-line offenders, partnering with a 3PL can quickly become a high priority. But how exactly are 3PLs able to provide rates lower than what a business would get on its own?
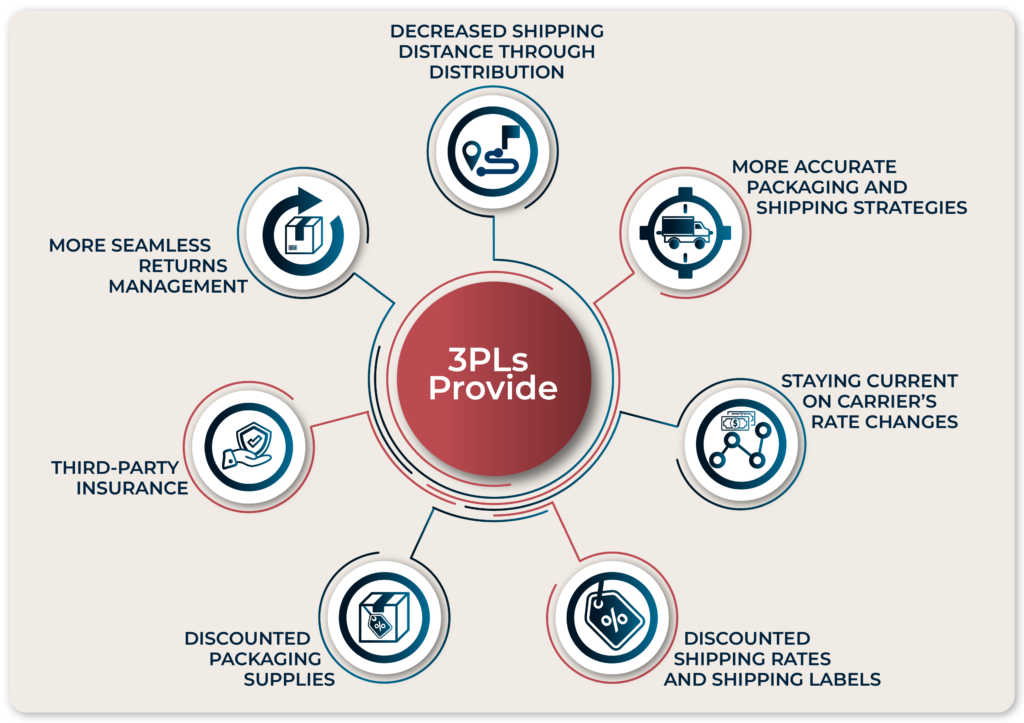
Decreased Shipping Distance Through Distribution
Shipping zones span from Zone 1 to Zone 9. Zone 1 starts with a 50-mile radius. The higher the zone, the more expensive it is to ship
How a 3PL Helps: Partnering with a 3PL can help a business ship strategically, eliminating higher shipping zones. 3PLs typically have strategically placed distribution centers across the country, allowing them to store and distribute products closer to their final destinations. By using their distribution centers, businesses can avoid shipping products to higher zones and receive better shipping rates.
More Accurate Packaging and Shipping Strategies
Shipping heavy items costs more if you’re not using flat-rate shipping. Many companies aren’t able to accurately size their shipments to get the best rates, resulting in higher costs.
How a 3PL Helps: Third-Party Logistics (3PLs) providers often handle a large volume of shipments from various businesses. This allows them to have expertise in optimizing the packaging process to minimize costs and reduce waste. One of the commonly used techniques by 3PLs is right-sizing packaging, which involves selecting the most appropriate box size for the product being shipped, eliminating unnecessary empty space while ensuring the safety of the product during transit. An experienced 3PL will know when to ship small, non-fragile items like clothing apparel in a less-expensive mailer envelope or poly bag, making the shipment more cost-effective.
Staying Current on Carrier’s Rate Changes
The major shipping carriers raise their shipping rates every year, tending to average about 5% over the previous year. These increases can vary by carrier, service level, weight, and other factors.
How a 3PL Helps: A 3PL keeps up to date on carrier pricing and can help a business get a better idea of how much they should charge a consumer for shipping (or how to adjust listed price to account for these rate increases).
Discounted Shipping Rates and Shipping Labels
This one is a bit of a no-brainer. Why would you pay list price when you can get a discounted shipping rate?
How a 3PL Helps: An experienced 3PL will offer discounts based on shipping volume, and you don’t have to ship hundreds of thousands of orders per month to qualify. Due to a history of loyalty, a 3PL can often negotiate volume discounts with carriers that pass on to their clients. In addition, a 3PL may purchase a certain number of shipping labels in advance, meaning you could cut your current shipping costs by up to 20%
Discounted Packaging Supplies
Businesses typically spend 10-40% of the product’s retail price on the packaging, which cuts into a large chunk of profit.
How a 3PL Helps: Just as they do with shipping rates, a 3PL will often have access to discounted packaging supplies. Partnering with a 3PL can save a company a lot of money on bulk packing supplies like boxes, dunnage, bubble wrap, airfill, and poly mailers.
Third-Party Insurance
Insuring goods in transit can add significant costs to the shipping process, especially for high-value items.
How a 3PL Helps: Partnering with a 3PL can allow a business to reduce shipping costs by cutting extra services such as shipping insurance, depending on the value of the product you’re shipping. A 3PL provider’s shipping insurance can often be cheaper than what a business could get on its own (by up to 50%).
More Seamless Returns Management
Returns cost a business a lot of money and stress, especially for high-volume brands.
How a 3PL Helps: The fulfillment side of 3PL services helps a business accurately fill orders. Partnering with a 3PL experienced in eCommerce fulfillment services can greatly reduce the number of returns. Return procedures can also be a challenge for companies to do on their own, and 3PLs leverage what is known as reverse logistics to manage this on a company’s behalf.
3PLs Serve as Strategic Partners for Growth
3PL shipping partners will typically pick orders from the warehouse in bulk, transfer them to a sorting facility, sort them based on their destination, and then forward them to the next shipping partner or directly to a consumer. As order volumes increase, the 3PL can staff up or down to meet the demand and flexibly devote more warehouse space as inventory needs go up. They often provide all packaging for shipping, like boxes, bubble mailers, and tape. By removing these obstacles for their business partners, 3PLs serve as a strategic partner for businesses, helping them grow without worrying about supply chain barriers that could slow revenue.

How Nautical Can Help Reduce Shipping Costs
- Importing & Exporting
- Container Drayage
- Less-Than-Truckload (LTL)
- Box Truck Delivery
- Full Truckload (FTL)
- Final Mile Delivery
3PL shipping FAQ
What is 3PL Shipping?
3PL shipping is a logistics and supply chain management practice in which a company outsources all or part of its shipping and distribution processes to a third-party provider. This approach can be particularly beneficial for companies looking to scale their operations or expand into new markets without the burden of managing all logistics aspects in-house.
What are 3PL Shipping Costs?
3PL shipping costs refer to the expenses associated with outsourcing various aspects of a company’s logistics and supply chain operations to a third-party provider. These costs typically include fees for services such as transportation, warehousing, order fulfillment, inventory management, and other logistics-related activities. The exact 3PL shipping costs can vary significantly depending on the specific services required, the volume of goods being handled, the distance traveled, and the 3PL provider’s pricing structure.
How To Reduce Shipping Costs?
To reduce shipping costs, businesses can negotiate favorable rates with carriers, optimize packaging to reduce dimensional weight charges, utilize shipping software for rate comparison, implement zone skipping or zone skipping strategies, consider regional carriers or local couriers, and explore freight consolidation options.




