Different manufacturing processes exist to produce the goods constantly being sold around the world. The product design and business needs of a company often necessitate the specific manufacturing approach that works best for them, and this can also vary by industry. Let’s cover the six primary manufacturing approaches factories use, and which might work best for your business.
What is manufacturing?
Manufacturing involves all the steps required to convert raw materials into a finished good (or into a component used in another manufacturing process). This process may involve a range of tools, people, and machinery. Manufacturing got its start with the technological innovations of the Industrial Revolution in the 19th century, which saw new machinery and chemical manufacturing processes combine with human labor to turn simple artisans into company wage laborers. Nearly 250 years later, innovation continues to spur further refinements and advancement, resulting in processes that increasingly make goods more and more globally accessible to businesses and consumers.
A company should decide on the production method based on factors such as demand, materials involved, and the resources available to them. Each manufacturing approach is unique and has certain distinct advantages to complete a certain production.
The 3 strategies of manufacturing production
Before getting into manufacturing methods, there are three manufacturing strategies that every manufacturer must decide between. The differences generally come down to when the goods or components are being fabricated. Products can be manufactured through a process that involves one or more of these production strategies: make-to-stock (MTS), make-to-order (MTO), or make-to-assemble (MTA). A successful manufacturing business requires a good mix of order volume, stock management, quality control procedures, and production operations cost optimization.
Make-To-Stock (MTS): This is the traditional process, where a factory produces a standardized product based on a forecast of demand. The inventory of the product is then held and distributed to retailers to meet consumer demand. Because demand is being predicted, the market for the goods needs to be established enough for the items to be produced ahead of time. Producing too much or too little results in high costs and missed revenue opportunities.
Make-To-Order (MTO): Instead of basing production volume on a prediction of demand, make-to-order manufacturing only happens after an order has been received (often involving a signed contract, like a purchase order). A manufacturer may develop custom samples as part of a custom product development process. Because large quantities of products aren’t being developed in advance, it is easier to manage inventories and react directly to demand in the market. But it also means that customers will have to wait for their products to be produced, so the manufacturer will need to continuously engage new clients to keep a steady flow of orders so that the factory remains profitable.
Make-To-Assemble (MTA): This manufacturing method involves the production of component parts in anticipation of orders for assembly. This helps the manufacturer prepare for orders they expect to come in and allows them to fill these orders more quickly when they arrive. But it can also leave them with a surplus of unwanted parts if demand doesn’t meet expectations.
The 6 common manufacturing methods
After choosing a production strategy, a manufacturer will next need to select the manufacturing method they will use to fabricate a product. These common manufacturing methods require different steps in the manufacturing process, and they can provide distinct advantages or disadvantages to a manufacturer making a specific good.
Repetitive Manufacturing
Repetitive manufacturing refers to a process that manufactures products repeatedly over a long period at a fixed production rate. Repetitive manufacturing is a very traditional concept, with dedicated production lines all working on the same product or component around the clock year-round. Because this process is running 24/7, it is great for companies that need large quantities of the same products in a short time. However, if the manufacturing of an item changes, it will lead to a tear down costing businesses time and money.
Batch production manufacturing
Batch production manufacturing is a semi-continuous process where products are manufactured in specified amounts and stored as batches. A batch production may consist of several steps separated by periods of storage or quality control checks. It allows similar or identical items to be produced together for different-sized production runs. Batch production shares similarities with discrete and job shop manufacturing methods, as it is driven by customer demand or the availability of ingredients and raw materials. It is ideal for companies wanting to ensure the quality of their products. Because this method involves individual product batches, there can be downtime between them and isn’t effective for a company needing constant production.
Discrete manufacturing
Discrete manufacturing runs on production lines and assembly lines much like repetitive manufacturing. However, instead of creating the same product every time, discrete manufacturing will often switch the setup of the machine to create custom products. The focus of discrete manufacturing is the production of distinct items through a process that can be divided into distinct steps or parts. Each step can be started or stopped independent of all the other steps, making it great for businesses that need flexibility in their design and production capabilities. Discrete manufacturing can be a very time-consuming process due to the number of different products being run through the system.
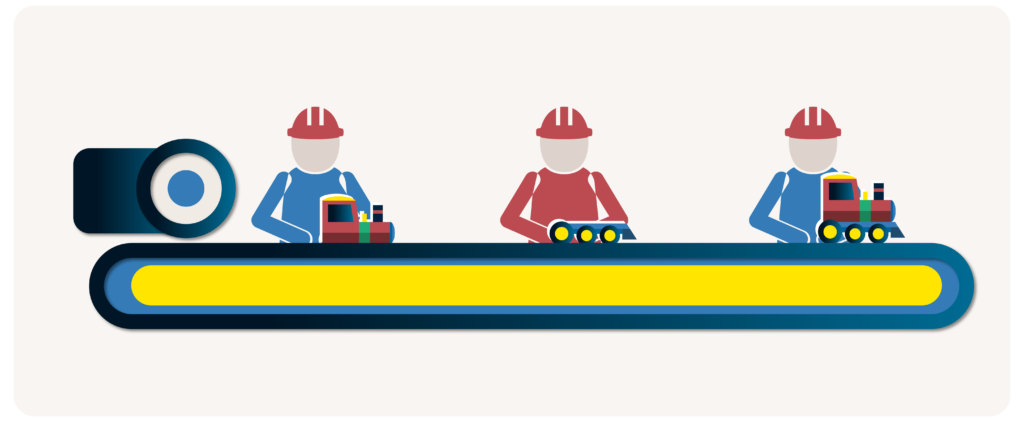
Job shop manufacturing
Job shop manufacturing uses production areas or workstations instead of an assembly line to create small-batch, custom-made goods with a heavy emphasis on product quality. Production phases can be carried out by individual fabrication shops containing craftsmen with the skills required to create that specific component. This process is great for the production of custom-built, quality products. Since it requires the use of trained operators, the production rate is slower than with methods.

Continuous production manufacturing
Like batch production, continuous production manufacturing is a process manufacturing method where the raw materials being processed are gasses, liquids, powders, or slurries, rather than solid materials. It is also known as flow production because the materials are continuously in motion. This process is very consistent and allows for an increased production rate due to it running 24/7. However, continuous production is very inflexible, and making changes can become very expensive and time-consuming.
additive manufacturing or 3D printing
3D printing is recognized as one of the newest manufacturing processes, gaining widespread use since originally introduced in the 1980s. Products are produced by layering various composites and materials (like plastics and metals), building each layer on top of the previous one to create shapes and patterns in a three-dimensional process. 3D printing is great for creating fast prototype products, helping greatly reduce waste. A large number of products today are being created using this process, including:
- Shoes
- Instruments
- Prosthetics
- Toys
When choosing to create products with 3D printing, it’s important to know your materials and build size are restricted. Not all raw materials can be temperature controlled for 3D printing. With 3D printing still relatively new, most print chambers are small. Any bigger items will need to be printed in smaller pieces and joined after production.
What is contract manufacturing?
When leveraging contract manufacturing, A company enters into a partnership with a manufacturer to outsource certain manufacturing processes. Contract manufacturing allows a business to take advantage of globally-available production facilities, and source goods at significant cost savings and other benefits.
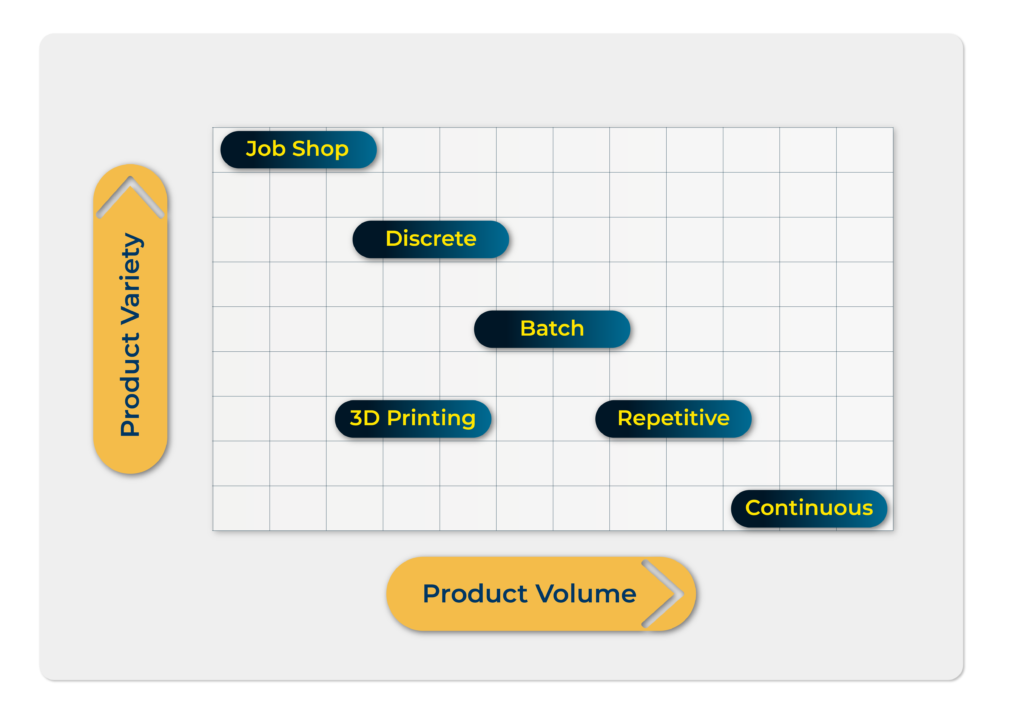
choosing a manufacturing method for your needs
There are many factors to consider when choosing a manufacturing method that will provide the best results for your products. Keep the following factors in mind when deciding on the production method that is best for your business.
- Budget
- Wastage
- Volume of Products
- Materials Used
- Product Dimensions
- Desired Quality
Fancy Food Inc. is a small food production company that specializes in making gourmet sauces and condiments. The company has been using a continuous manufacturing method for many years to produce its products. However, the company recently received a large order from a supermarket chain, and the production team realized that they would need to switch to batch manufacturing to meet the fluctuating order volume required by the retailer.
Batch manufacturing involves producing a specific quantity of a product at one time before moving on to the next product. The process is ideal for companies that have fluctuating demand or need to produce a variety of products.Example
Manufacturing with Nautical
In today’s fast-paced business environment, it’s crucial to prioritize quality and efficiency in every aspect of your operations. At Nautical, we understand this better than anyone. As a company that leverages a global supplier network of contract manufacturers, Nautical’s direct relationships and streamlined processes enable us to deliver high-quality products to our partners in the most cost-effective way possible.
Our international teams of sourcing specialists work tirelessly to identify the most competitive regions for each product category and manufacturing process. By expanding our network to include suppliers from all around the world, Nautical can tap into manufacturing regions with significant economies of scale and low production costs to pass those savings on to our partners.
But our commitment to quality doesn’t end there. We provide on-site quality control inspections for every production run to ensure that there are no issues that could impact the final product. This approach not only ensures that our partners receive the highest quality products, but also enables us to detect and correct any issues before they become major problems. In addition, we provide comprehensive 3PL and fulfillment services here in the United States to help streamline our partners’ operations. By working with Nautical, you eliminate the need for multiple partners, reducing complexity and improving efficiency.




